We all know an SSL certificate helps in verifying a website. But, hardly anyone knows it can help in verifying a client as well. Similarly, most people are unaware that one can install it on the PC besides installing it on servers. Therefore, it not only helps in identifying real businesses online but also in finding genuine clients. In simple words, SSL/TLS client authentication has the same value for client verification as is its web version for online businesses. We will here explore various aspects of SSL/TLS Client Authentication in this article.
What Is SSL/TLS Client Authentication
In this type of verification, the client produces a keypair to validate it with a selected server. In this process, the personal key of the certificate stays with the client and not with the server. However, it is also saved in the browser. The task of the server is to verify the private key a customer has. After validation, it gives permission a safe and sound communication between two parties.
How does an SSL/TLS Client Authentication work?
Both, the client and server certificates look almost the same type of digital certificates as they contain clients as well as server applications. However, they have many differences in their work. For example, in the case of a server authentication certificate, a client receives the server certificate at the start of each session. The client then utilizes it to validate the server. On the other hand, in the client certificate, the server rather than the client receives the authentication certificate at the start of the session. The server then utilizes it to validate the client.
In simple words, SSL/TLS client authentication is among the tools which help apps to recognize the validation of server certificate. It also assists the businesses in finding if the client has a genuine certificate. However, it is important to know that it doesn’t provide any information about the client if it is trustworthy or not.
SSL Server Certificate Authentication vs SSL Client Certificate Authentication
In order to make a safe connection between two persons or parties, an SSL handshake is necessary. This handshake is important to carry out validation and to discuss the protocol ciphers that play a crucial role after making the connection. Normally, when the client visits a website, it is the server that shows its certificate, and the client is the one doing the validation task. This action takes place after multiple verification steps. These steps include:
- The digital signature is trusted
- Timestamp validation
- OCSP/CRL is not revoked
- CT logs are proper
However, in the case of SSL/TLS Client Authentication, both sides follow the validation procedure. When the server shows its certificate, the client shows its own. After it, the client and the server both validate the certificate. This way the handshake between the client and server takes place. It’s an extra step, that takes place in the back-end, and normally doesn’t increase latency.
To fully understand client SSL, it is necessary to have basic knowledge of SSL handshake.
Client Handshake
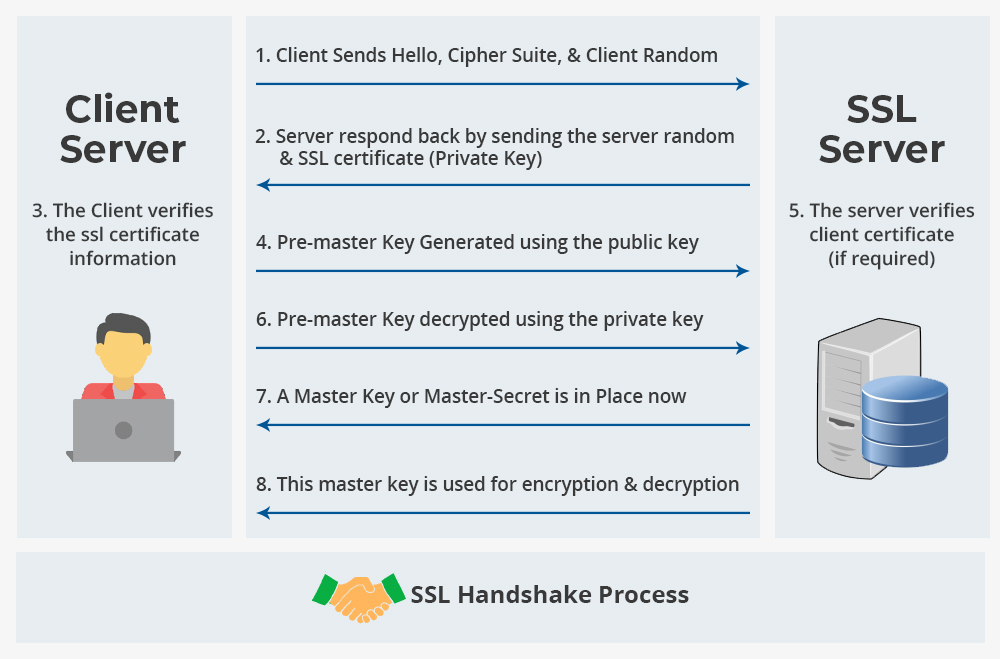
In the client SSL handshake, the conversation starts with client hello and server hello messages in response. The server asks the client to provide the certificate. After the client provides it, the server then checks and verifies it. After this step, encryption completes with the help of symmetric encryption. This handshake normally consists of up to 8 steps. See the following figure to understand it.
Uses of SSL/TLS Client Authentication
Its use is common where a business wants to give access to verified users only. Therefore, it plays a role against the attacks coming from outside users. As we know, hackers use various tricks to steal the user’s data and passwords alone are not enough to protect it. Therefore, the use of two-factor authentication is increasing with time.
This is where client authentication plays its role. We can minimize password usage because in client SSL only the client knows the private key. However, it is wise to use a password along with client SSL. This is called two-factor authentication. It will ensure that you get the best results for data protection.
Another use of SSL/TLS client authentication relates to IoT gadgets. In a bigger IoT infrastructure, the chance of unauthorized access reduces with the use of client SSL as an owner can issue only a single certificate for one device.
Why the SSL/TLS Client Authentication is Not So Popular
The client GeoTrust True BusinessID Multi-Domain SSL has many advantages, but when we study it in-depth, we can found some of the disadvantages easily. Due to these disadvantages, the client SSL is still not as popular.
Less Convenience
The browser has an SSL client certificate saved in them. This restricts its utilization to one specific system. This is particularly inconvenient when we have more than one device under our use.
Complex for Common Users
Installing an SSL certificate on a device is not easy. The servers can hire professionals to install it. However, for a common user, it is a tough task to complete.
Two-factor authentications
To deal with the disadvantages of using passwords alone, people and companies are moving to two-factor authentication. MFA is easy to use the client SSL. Therefore, companies are preferring MFA rather than the client SSL which is complex to use.
The Final Words
The client SSL is a good new idea. The biggest advantage of client SSL is two-factor authentication. In client SSL, two-factor verification doesn’t require sending a text or an email like in other methods. The client SSL is installed on a device that is required to connect with any server or a site. Here the client SSL acts as one part of the two-factor verification. This way, it helps the users to only put their password and move to what they want to open.
Currently, two-factor authentication is easy to use without creating hurdles for the workers and end-users. The difficulty to use is one of the most widely mentioned reasons for not following security best practices. Decreasing this difficulty by using client SSL is a good step. It’s also the most economical way to achieve two-factor authentication.

